Menu

We offer both generic and fully customized training. All courses can be accessed using various devices such as smartphones, tablets and PCs at home or in the workplace. The focus is to develop and deliver high-quality learning, with interactivity and engagement reflected in all the online content that is created. Courses can be uploaded to our Learning Management System so that all delegates can utilize the courses in one common place.

The learner is able to move seamlessly from the digital training environment to their real- life workplace, having already learned about the layout and safety areas of their workplace and the procedures and forms they need to adhere to. Specific skills on the equipment found on their vessel will have been developed on the same manufacturer’s equipment during interactive workshops and the learner’s skills on this equipment can be further tested through the performance of a number of tasks in the workplace.
All custom courses are competence assessed as meeting the required standard. Our teams work with every client to ensure that the training is certified to the appropriate international standard and fulfils any specific requirements.
Safety-related topics that require mandatory training in order for delegates to be able to work at sea or offshore. Training courses filled with highly interactive digital content, supported by practical training and workshops, to achieve the required standards and certification. We ensure that all course content is kept up-to-date with ongoing developments in technology and updates to applicable marine and safety legislation. All courses are based upon the STCW standards and guidelines from the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and Merchant Navy Training Board (MNTB).
All maritime training courses address all of the required learning outcomes from the standards and present the training content in the most time and cost-effective way, while maintaining the highest standards of interactivity and learner engagement. Courses are assessed according to the standards, using a variety of online and competence-based assessments. Certification is made in accordance with the Awarding Bodies and also offering subsequent refresher training to the same standards that will maintain the learners’ knowledge and skills.
All e-learning courses can be branded with a client’s logo and customized to accommodate client-specific vessels, operations and procedures. Although courses are presented in the English language, they have been designed to be easily translated into multiple different languages, if required. End of Course Assessments and a Practical Workbook is included with each title.
Duration: Typically 30-240 minutes
Languages: English (translation into additional languages is straightforward)
Frameset: Featuring buttons to allow:
Standard: SCORM 1.2 and above
Media: Rich media mix to include:
Assessment:
Case Studies: Marine case studies relevant to the course subject
Question Types:
Certification: Learners who pass the assessment will receive a Ponant certificate.

Duration: 180 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
The learner understands the principals involved in controlling firefighting operations on board a vessel.
The learner is able to control firefighting operations aboard ship.
The learner is able to organize and train fire parties.
The learner knows how to inspect and service fire detection and extinguishing systems and equipment.
The learner is able investigate and compile reports on incidents involving fire.

Duration: 180 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 150 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
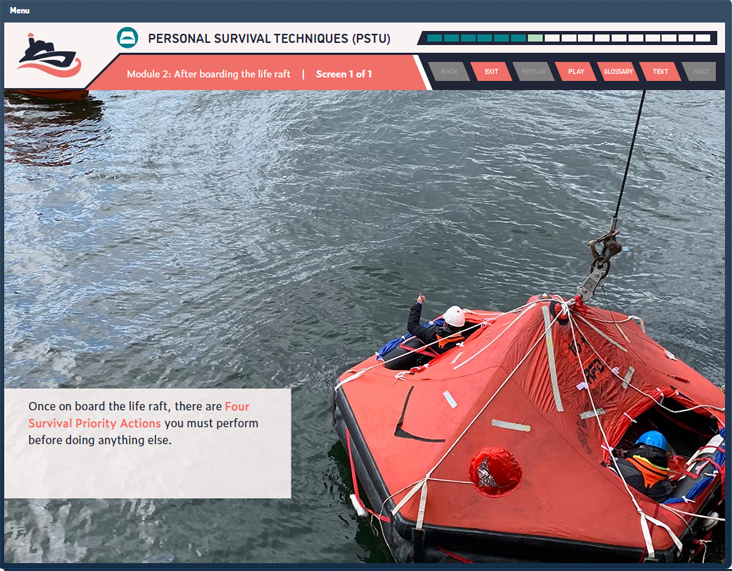
Duration: 150 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 240 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 20 Minutes
Duration: 180 Minutes
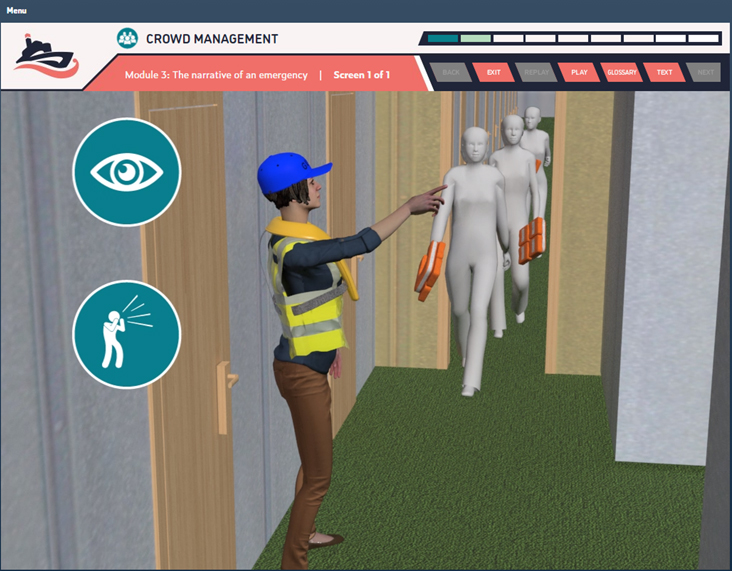
Duration: 90 Minutes
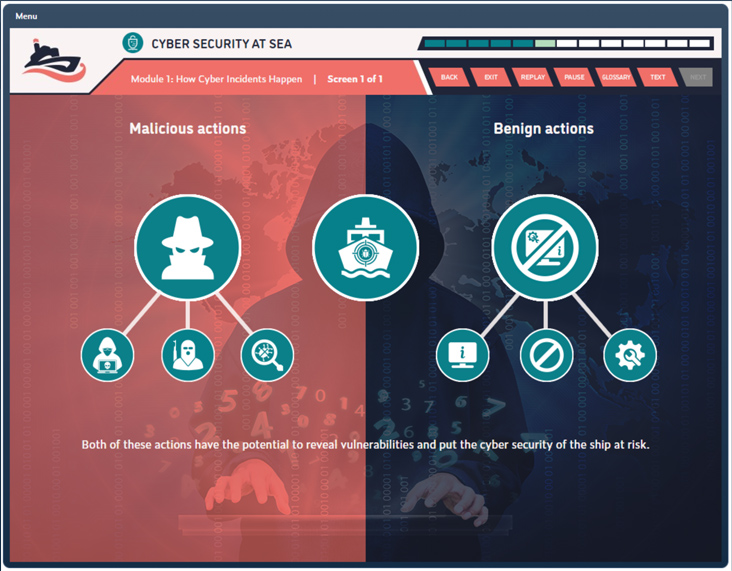
Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 120 Minutes
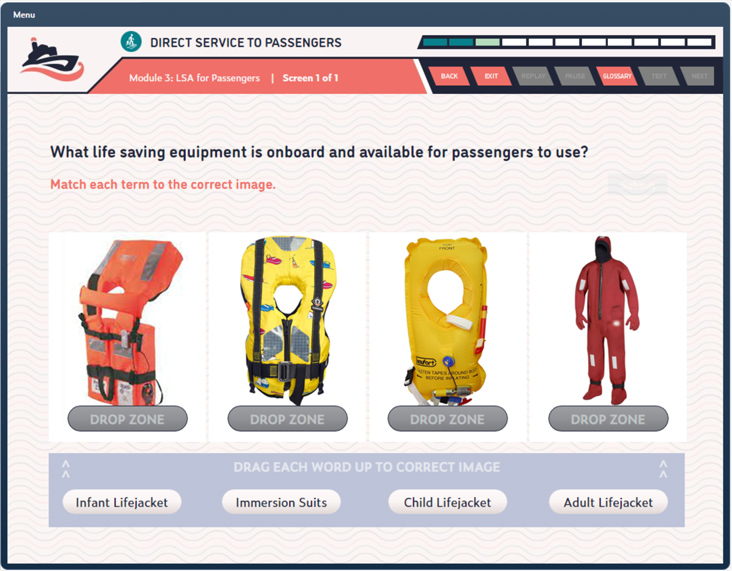
Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 120 Minutes
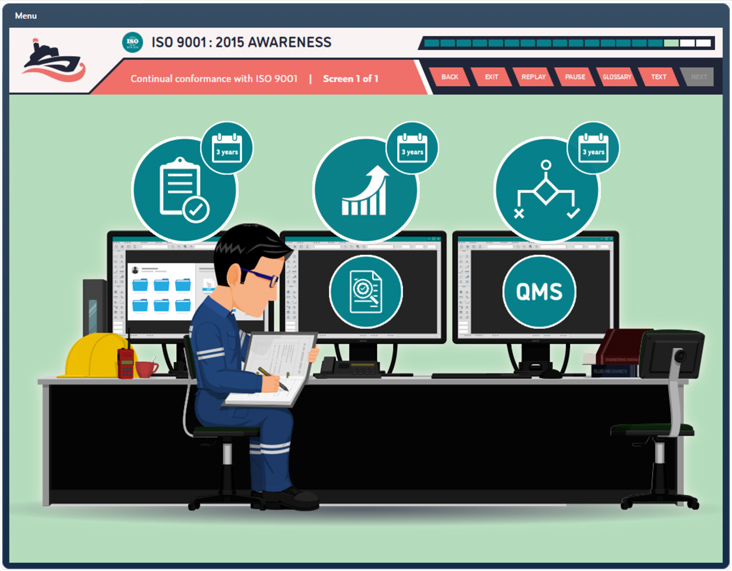

Duration: 20 Minutes

Duration: 30 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 60 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 180 Minutes

Duration: 120 Minutes
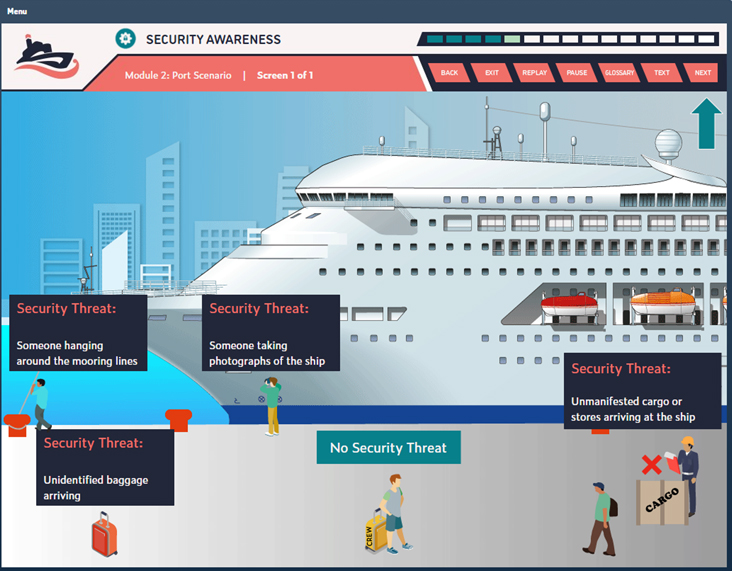
Duration: 180 Minutes

Duration: 30 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
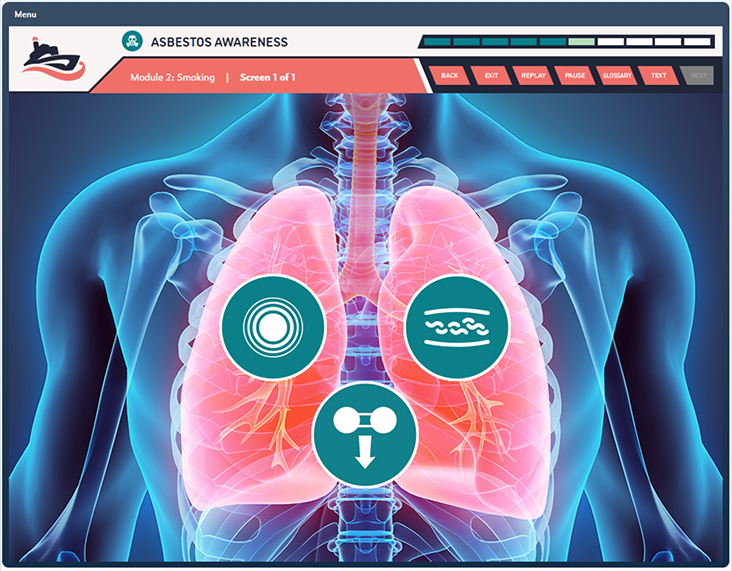
Duration: 30 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
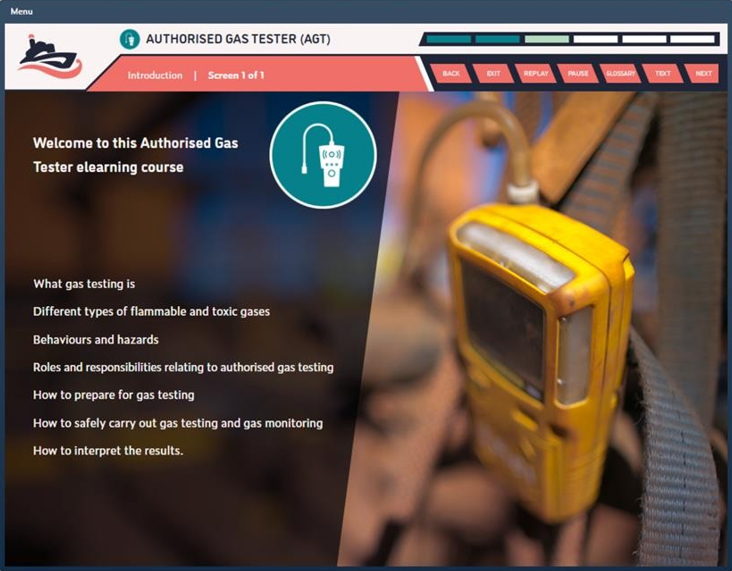
Duration: 120 Minutes
Duration: 30 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Duration: 30 Minutes
Duration: 180 Minutes

Duration: 90 Minutes
Duration: 60 Minutes
Duration: 60 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
Duration: 60 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes
Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 30 Minutes
Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 90 Minutes
Duration: 180 Minutes
Duration: 60 Minutes

Duration: 20 Minutes
Duration: 180 Minutes
Duration: 60 Minutes
Duration: 20 Minutes

Duration: 90 Minutes

Duration: 20 Minutes
Practical Workbook: Yes

Marine Simulation training uses technology to create environments to train ship’s officers, pilots and a range of other senior maritime professions in the safe and competent operation of the navigational bridge, electronic charting systems, dynamic positioning stations and liquid cargo transportation systems.
Our teams work with the largest maritime and marine companies in the world to deliver navigational assessment and simulated bridge and ECDIS operations using the latest technology. This technology presents simulated environments that challenge the delegate with a range of hazards, system failures and challenging human element scenarios that require the delegates to demonstrate competence in their knowledge of the systems and of the correct procedures to follow to avoid critical failures from occurring.
Courses meet the STCW standards and are developed to include client-specific information such that the training is wholly relevant to the delegates and prepares them to move from the simulator training straight into real-world marine operations.
Maritime simulation technology simulates and overcomes navigational and leadership challenges. These courses are 3-5 days duration and involve instructor-led delivery via webinar, supplemented with simulation sessions on the learner’s own PC – controlled by the instructor – to allow competence-based work to be performed and assessed.
Simulation courses can be run in a physical environment, with delegates attending lecturer-led training and simulation sessions. We deliver online simulation courses that use exactly the same materials and deliver the lecturer-led presentations via interactive webinars, and the simulation training online with delegates being able to access the simulator software, and perform exercises, from the comfort of their own home or office.
All marine training materials have been developed by Master Mariners who have also worked as lecturers for various International Maritime Academies and are recognized as meeting the STCW standards.


This 5-day course is delivered using a blend of online webinar and online simulation training and meets the STCW standard. The course is customized to reflect clients’ operations, vessels, procedures, work instructions and equipment.
This course provides training to Navigation officers to operate ships in Polar waters and to address those additional provisions deemed necessary for consideration beyond existing requirements of the SOLAS and MARPOL Conventions, in order to take into account, the climatic conditions of polar waters and to meet appropriate standards of maritime safety and pollution prevention.
This course is designed to meet the Mandatory Minimum STCW requirements for the training and qualifications of Masters and Deck Officers on ships operating in polar waters, by the 2010 Manila Amendments, specifically as these apply to tables A-V/4-2.

This 4 ½ day course is delivered using a blend of online webinar and online simulation training and meets the STCW standard. The course is customized to reflect clients’ operations, vessels, procedures, work instructions and equipment.
This course provides training to Navigation officers covering advanced requirements to operate ships in Polar waters and to address those additional provisions deemed necessary for consideration beyond existing requirements of the SOLAS and MARPOL Conventions, to consider, the climatic conditions of
polar waters and to meet appropriate standards of maritime safety and pollution prevention.
This course is designed to meet the Mandatory Minimum STCW requirements for the training and qualifications of Master’s and Deck Officers on ships operating in polar waters, by the 2010 Manila Amendments, specifically as these apply to tables A-V/4 and IMO Model Course 7.12: Advanced training for ships in polar waters. All aspects defined in IMO Polar Code and Model Course will be covered.

This 5-day course is delivered using a blend of online webinar and online simulation training and meets the STCW standard. The course is customized to reflect our clients’ operations, vessels, procedures, work instructions and equipment.
This course provides training to Navigation officers covering basic and advanced requirements to operate ships in Polar waters and to address those additional provisions deemed necessary for consideration beyond existing requirements of the SOLAS and MARPOL Conventions, to consider, the climatic conditions of polar waters and to meet appropriate standards of maritime safety and pollution prevention.
This course is designed to meet the Mandatory Minimum STCW requirements for the training and qualifications of Masters and Deck Officers on ships operating in polar waters, by the 2010 Manila Amendments, specifically as these apply to tables A-V/4 and IMO Model Course 7.11 and 7.12: Basic and advanced training for ships in polar waters. All aspects defined in IMO Polar Code and Model Course will be covered.

This 3-day course has been developed to reduce the risk of accidents at sea and improve the effectiveness and decision-making of the Bridge Team.
The focus is on team dynamics and human error and also on increasing operational uptime and daily efficiency. The course is delivered using simulators, either in a physical environment or also online using web-based simulation software for the simulation exercises and webinars for the instructor-led elements.
In the simulator, officers are trained to deal with dynamically escalating situations emphasizing the need to apply the learning in real life situations. The participants are provided with tools to improve teamwork, leadership, communication, decision-making and resource management.
The course is customized to reflect our clients’ corporate values and operations so as to make the training entirely fit for purpose.
The delegates will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of resource management, leadership and teamwork to fulfil the requirements of STCW 2010, Sections A-II/1 and A-II/2:

This 5-day course is delivered using a blend of online webinar and online simulation training and meets the STCW standard.
This course meets the requirements laid down in the STCW Convention, 1978, as amended (Manila Amendments), section A-II/1, Table A-II/1, satisfying the requirements for an understanding and competence of bridge team and resource management.
The aim of this training course is to further the competence of a Deck Officer of the Watch, Master Mariner, Chief Mate or Marine Pilot in regard to bridge teamwork, ship handling and operational management. The aim of the training is to equip the candidate with the knowledge and skills needed
to keep a safe navigational watch onboard while operating in a bridge team.
On completion the candidate will have demonstrated competence of bridge team management that will aid in the safe navigation of a vessel in open and confined waters and in normal and emergency situations. The publication MODEL COURSE 1.22 – SHIP SIMULATOR AND BRIDGE TEAMWORK (2002 Edition) was primarily consulted for the development of this course.
The delegates will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of resource management, leadership and teamwork to fulfil the requirements of STCW 2010, Sections A-II/1 and A-II/2:

This 5-day course is delivered using a blend of online webinar and online simulation training and is approved as meeting the STCW standard.
The course is customized to reflect our clients’ operations, vessels, procedures, work instructions and equipment.
This course provides training in the theory and use of Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS) for those who will be in charge of a navigational watch on vessels equipped with ECDIS. The training comprises all safety-relevant aspects and; for this reason, aims beyond the use of operational controls. Theoretical aspects including all major characteristics of ECDIS data such as data contents and all major characteristics of the display of ECDIS data will be covered in sufficient depth. This will be completed through both practical and theory training and to address those additional provisions deemed necessary for consideration beyond existing requirements of the SOLAS.
This course is designed to meet the Mandatory Minimum STCW requirements for the training and qualifications of Masters and Deck Officers on ships operating in polar waters, by the 2010 Manila Amendments, specifically as these apply to tables A-II/1-3 and IMO Model Course 1.27: The Operational use of Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS).
The delegates will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of resource management, leadership and teamwork to fulfil the requirements of STCW 2010, Sections A-II/1 and A-II/2:

This 3-day course is delivered either as an online or physical simulation. The minimum number of delegates per course is 4; the maximum is 6. BMA certification is not required for this course.
The course is customized to reflect our clients’ operations, vessels, procedures, work instructions and equipment.
The training comprises all safety-relevant aspects and, for this reason, aims beyond the use of operational controls. The purpose of the Ship to Ship (STS) training is to train captains and officers as wells as pilots or mooring masters in advanced ship maneuvering techniques during STS operations by improving communication and mutual understanding between the captain of the mother vessel and the pilot or mooring master on the daughter vessel during maneuvering. This is ensured through theory and simulator exercises, and in that way a high level of skills in relation to close quarter STS operations is ensured.
The course will contain ongoing monitoring of the delegate’s performance and a final assessment.
Creating the optimum blended learning program requires a careful review of all the theoretical and practical elements needed to meet the learning outcomes. The Team of Course Designers consider all forms of training and learning to create the most effective learning and assessment program, which can be completed in the shortest timeframe and most flexible manner at the lowest total training cost.
The pedagogy of each course will be determined by many factors, including the profiles of the learners, their ability to use technology, and the standards and certification required.
Prior to entering a training course or syllabus, there may be pre-learning required to ensure that all delegates arrive at the course with a common standard of theoretical knowledge. This ensures that the practical and workshop-based training can be conducted at a pace where no delegate is “left behind”. Pre-learning can include self-study using online resources, undertaking online e-Learning courses to learning theoretical concepts or mentoring sessions with an experienced professional in the field.
Pre-assessment is used to ensure that delegates who have had to complete pre-learning have gained the theoretical knowledge required for them to participate in more advanced training. Pre-assessment is also used to ensure that delegates who are experienced in the field, actually have the knowledge required on the specific subject matter that the training course will cover. Pre-assessment can be conducted using online assessment tools and for safety-critical subjects, may occur at the training facility prior to the training taking place.
Digital Learning can take many forms, including e-Learning courses and micro learning, where delegates are given access to nuggets of information relating to a specific subject or item of equipment. This allows for targeted learning aimed at specific, predefined learning outcomes. Using online simulation and online assessment tools along with a wide range of assessment techniques, the knowledge of the learners is determined. Our teams specialize in developing highly interactive online courses that use a wide variety of media techniques including immersive 3D environments, AR/VR, animations and high quality video, to provide the learner with a learning environment that reflects their own place of work. All online offerings are optimized for delivery in low bandwidth environments.
The experience and presence of an instructor can be a key element in enabling delegates to develop skills and competences. Our instructors deliver interactive workshops and guide delegates through task-based activities that are aimed at creating competence in the delegates. Basic theory is delivered online and our instructors focus solely on task-based training and the competence assessment of delegates. This ensures that the total time of a training course can be minimized, with theoretical content delivered online and instructors using their skills where they are most effective – on skills-based training, not delivering PowerPoint presentations.
We use instructors to train delegates on a wide-range of subjects from mandatory and life-critical safety training skills to mechanical and electrical installation, inspection, repair and maintenance routines, and other technical courses. We have relationships with a number of equipment manufacturers of items such as electrical systems, mechanical equipment, refrigeration systems, instrumentation systems, safety systems, IAS and cryogenic and pressurized gas systems. Each course is tailored specifically for each client to reflect their equipment, procedures and safety management system.
It is vital for delegates to be able to take the skills they have learned online and in a workshop environment, into their workplace such that they can perform their roles safely and to the required level of competence. We can provide Competence Assessors and External Verifiers to attend vessels and assets to assess the competence of crew performing specific tasks to a pre-agreed standard. We can help to develop competence standards and systems for our clients, if required, or work with whichever competence system they already use. We can also create workbooks that stipulate a number of competence based-activities for completion by the delegate in their workplace, under supervision from a Qualified Person, which may then be externally verified by our group’s Verifiers onshore.
Many training courses, especially concerning mandatory safety subjects, require to be refreshed in accordance with the relevant standard. Our group has created innovative, blended learning models that maximize the use of online learning to enable refresher training to be as flexible for the learner as possible, while minimizing training costs for the employer and the delegate. Delegates’ knowledge and skills are assessed online such that the refresher training can focus very much on the individual knowledge gaps of each delegate. Where possible, all refresher training can be undertaken via smartphone to ensure maximum flexibility.
We work with a number of Internationally, recognized certification bodies to ensure the training we deliver has value and portability for the successful delegates. We also work with our clients to create tailored learning materials that are specific to their operational requirements and to then have these certified to an international standard, ensuring that the highly customized and appropriate training is also certified to an Internationally-recognized level.
Developing your personnel is not simply a case of sending them on a number of industry-mandated training courses. Each employee in your business will have specific knowledge, skills and experience and will have aspirations for their career development. We work with our clients to streamline not only the mandatory training, but also to develop a learning and safety culture that drives best practice across the workforce.
We ensure that all of the required training and competence development takes place across your entire enterprise, while addressing organization-specific and individual-specific gaps in knowledge, skills and competence. Our teams have worked with some of the largest maritime businesses in the world to improve compliance and competence across their organizations and to instill a robust and motivational learning culture.
Our work also involves analyzing every cost element of the training delivery and working with our customers to improve the quality of the learning while also optimizing the total training cost.
Getting the right training, at the right place, at the right time and the right cost
Companies can face significant challenges in determining the training required across their workforce to ensure all personnel are not only compliant with the required international legislation, but are also competent to perform their roles. This can include variations for different classes of vessels operating in different global regions. Our team of learning and development professionals work with our clients to define the skills and competences for all roles included in the training matrices for all types of vessels ensuring that effective training that develops these skills and competencies, has been identified and is available. This will include mandatory training, development training, region-specific training, vessel-specific training and equipment-specific training. This training will ensure that each learner has the required knowledge and competencies to perform their roles safely and in compliance with the applicable legislation.
Developing the attitudes, skills and experience to excel
There are many different competence standards used across the maritime industry, some based on international standards that have been created by Awarding Bodies and some developed in-house to address specific, niche roles that perform a range of specialist activities. Our team can assist in developing the standards, to ensure that specific roles have clearly defined competencies that align with best practice and accepted safety standards and can also develop online competence management systems that will allow the competencies of all personnel across the enterprise to be viewed in real time. Clients can view their compliance percentages across roles, assets, projects, regions and other pre-determined criteria. Individual competence portfolios may also be managed, updated and stored to ensure easy access to all competence and compliance information required by the regulatory authorities.
Ensuring all learning outcomes are achieved using the most effective training solution at the lowest total cost
Our teams have has worked with several global marine businesses to assist in optimizing their training operation by:
This work can be performed remotely or by placing a specialist in-house to support the clients’ Training and Development Departments.
At Global Training Solutions Inc., we provide learning solutions for your specific organizational needs. Get in touch and let us help you create a high-impact training and development program.