

WATPRO is a sophisticated water treatment simulator for predicting water quality. It allows for simple evaluation of the performance of a drinking water treatment facility from a microbial and chemical standpoint.
The simulator uses the EPA-developed CT approach to calculate chemical inactivation of Giardia and viruses while simultaneously estimating formation of DBPs. Using raw water quality parameters such as pH, TOC and SUVA, chemical dosages (e.g. alum, ferric chloride, lime , ammonia) and design and operating characteristics of process tanks, WatPro accurately simulates plant operation.
WatPro has a user-friendly interface that allows a schematic of the water treatment plant to be easily configured within minutes.
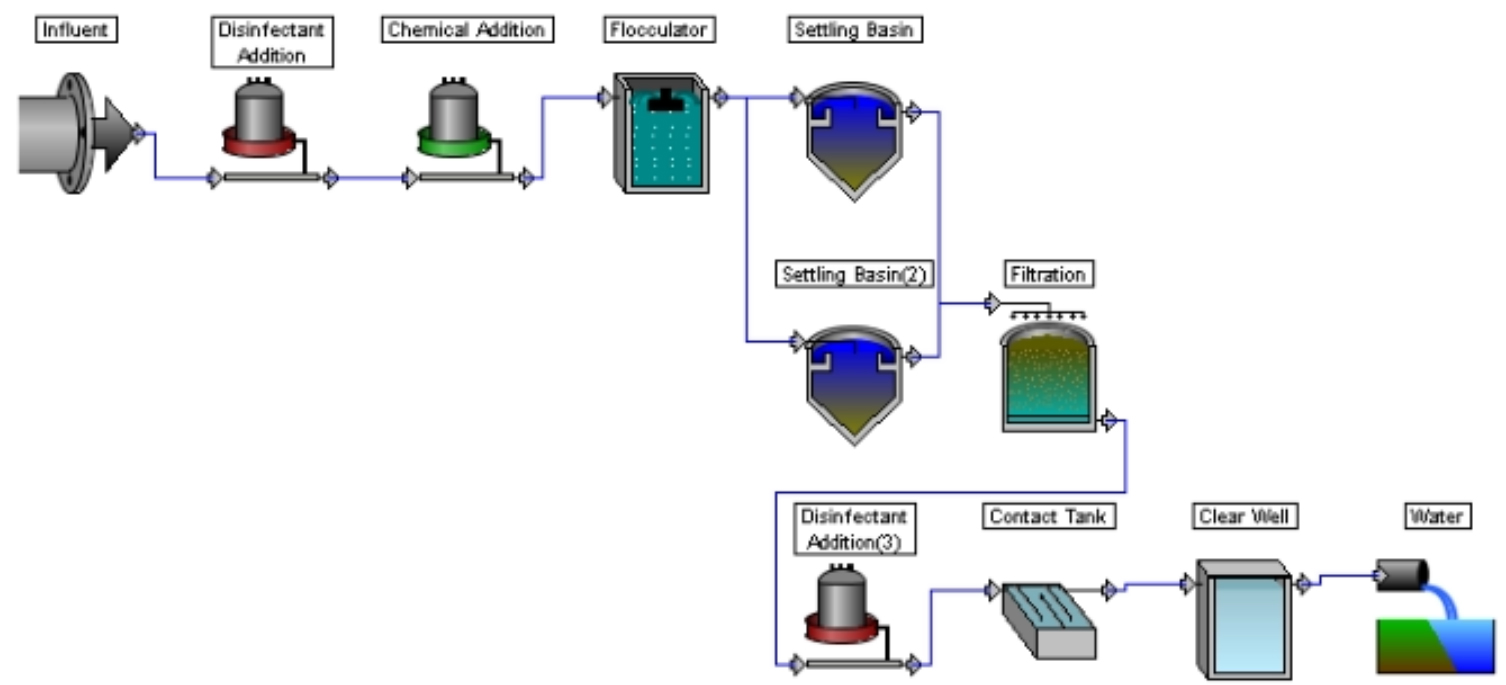
The substitution of chlorine by chlorine dioxide as a disinfectant in drinking water treatment is of growing interest. While chlorine has been effective for reducing most microbial pathogens to safe levels, it reacts with naturally-occurring matter in the water to form trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs) as disinfection by-products (DBPs).
In WatPro, the models for consumption of ClO2, and formation of chlorite and chlorate are taken from newly published university research. The expressions are expressed as functions of water quality and chlorine dioxide related parameters.
WatPro is very useful in the evaluation of the substitution of chlorine by chlorine dioxide. Through modeling, one can determine microbial reductions and levels of DBPs formed at comparable disinfectant doses. Once the doses of disinfectants are known, cost comparisons may be conducted to see which is the most cost-effective
WatPro can show whether pathogenic bacteria like E. coli 0157:H7 have been adequately inactivated in a water treatment plant.
For an uninterrupted primary disinfectant dosage rate, WatPro tracks the inactivation of viruses and Giardia by disinfectant addition. Because fecal coliform bacteria are inactivated by disinfectants to a greater extent than viruses, the log reduction of bacteria like E. coli will match or exceed the reduction for viruses calculated by WatPro. The simulator also determines the Ct disinfection parameter at any location in the treatment plant